Helium
INDUSTRIAL HELIUM GAS
Interesting Facts & Information About
Helium (He)
Helium (He) is a colourless, odourless, non-toxic, non-corrosive and non-combustible gas. It is mainly sourced from natural gas wells. This valuable gas is in short supply the world over, which is why many applications incorporate recovery and recycling systems.
With the lowest boiling point of any gas (4.2 Kelvin or –269° Celsius), liquid helium is the coldest matter on Earth. This makes it ideal as a cryogenic agent for a number of cutting-edge medical and physics applications. For instance, it is used to cool superconductive magnetic coils in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) medical equipment.
In fact, helium is indispensable across a wide range of industries. For example, it is used to pressurise rocket fuel; create inert atmospheres for welding, heat treatment and epitaxial crystal growth; purge semiconductor atmospheres; calibrate analytical instruments; inflate airplane tyres and airbags; test for leaks; inflate large balloons for meteorological studies; and fill electronic tubes in neon signs.
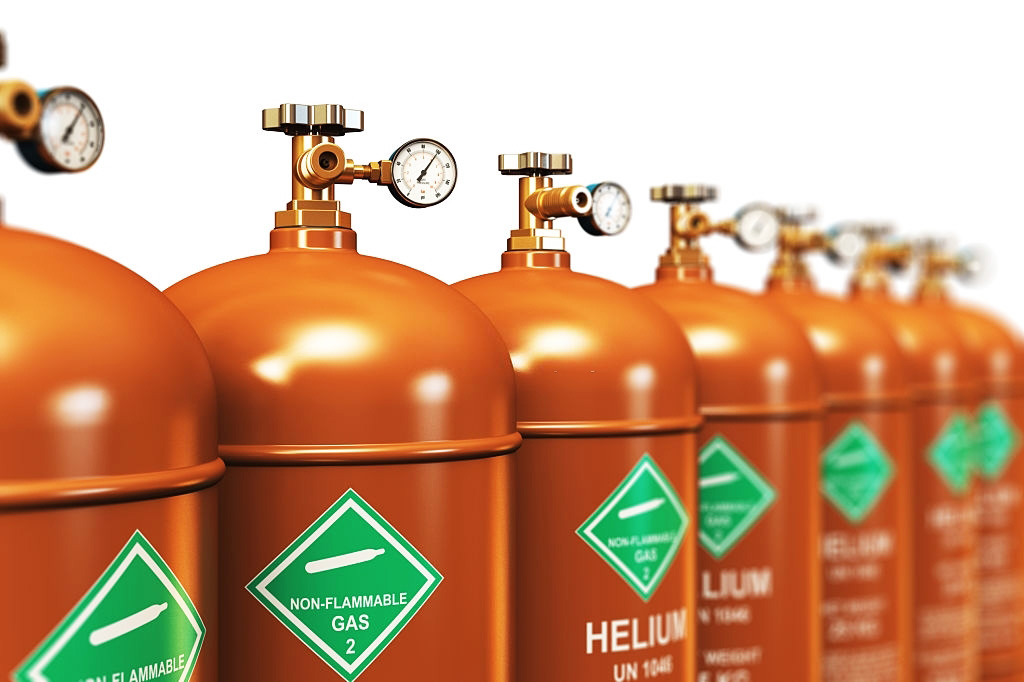
Depending on your volume requirements, we can supply helium in special insulated ISO containers, tube trailers, dewars, multi-cylinder packs (MCPs), regular cylinders or portable cylinders.

Supply Form
Cylinders
Cryogenic
Cylinder
Mini Bulk
Bulk On Site
ASU Plants
Application of Helium (HE)
USES OF HELIUM GAS AND LIQUID HELIUM (HE) BY INDUSTRY

Diving Breathing Mixtures

Welding Processing

Healthcare Services

Leak Detection
Electronics

Scientific Uses
Allied Products




Allied Products
Allied Products
Allied Products
Allied Products
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry.
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry.
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry.
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry.
Related Videos/Downloads
Download Brouchure
To enrich air and increase combustion temperatures in blast and open hearth furnaces; to raise steel temperatures in steel making.
Download Brouchure
To enrich air and increase combustion temperatures in blast and open hearth furnaces; to raise steel temperatures in steel making.








